1. Everyday conversations
Engaging in day-to-day dialogues is an effective way to acquire colloquial language, idiomatic expressions, and authentic English. For individuals who are keen on advancing their language proficiency, provides a valuable resource that offers concise audio conversations with corresponding transcripts, tailored for various real-life scenarios.
Practice with scenarios like these to become familiar with what vocabulary you might encounter, everyday conversations are usually light-hearted and uncomplicated so there's little pressure if you make a mistake in a real-life chat.Ěý
2. Job interviews
If you're looking to improve your performance in job interviews or looking for a job within an English company, it can be incredibly helpful to practice various possible scenarios beforehand, giving you time to practice your language skills. This way, you'll be better equipped to communicate your experiences, skills, and future aspirations in a clear and concise manner.
has compiled a list of commonly asked interview questions, each one accompanied by sample answers that can assist you in your preparation process. There are lots of with prep questions available online. Whether you're a seasoned job hunter or just starting out, taking the time to review these questions and answers can go a long way in boosting your language confidence and success during your next real-life interview.Ěý
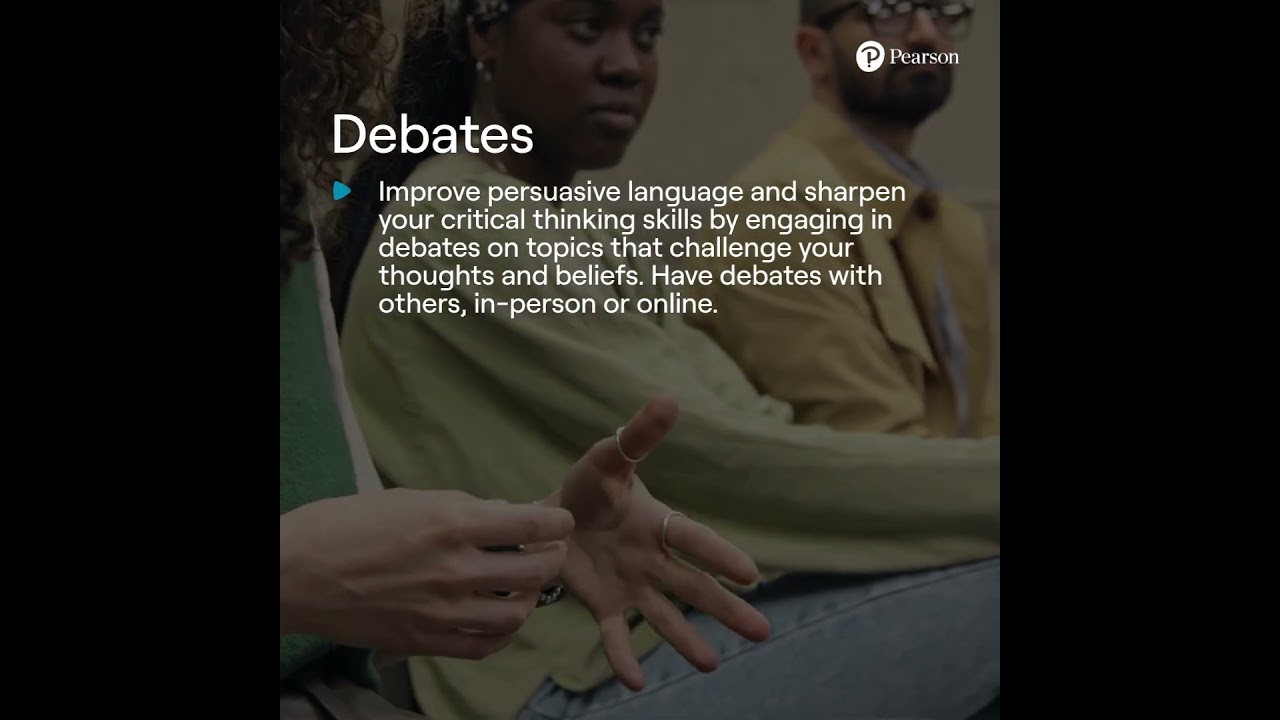
3. Role-playing debates
Enhance your ability to use persuasive language and sharpen your critical thinking skills by engaging in debates on topics that challenge your thoughts and beliefs. With , you have access to a diverse selection of debate topics and resources that are specifically tailored to meet the needs of ESL learners. Take advantage of debate opportunities to broaden your perspective and develop valuable communication skills.
You could have debates with friends, family or online. If you don't feel confident enough to debate with others, you can also look at existing debates online and on TV and construct a theoretical argument in English to go against or support their points.
4. Travel simulations
Practicing travel scenarios can assist you in improving your ability to ask for directions, book accommodation, and communicate with locals. You might intend on working abroad in an English-speaking country and need to travel a lot. If you are looking to improve your airport-related vocabulary and phrases, you can find videos of various travel scenarios like Ěýthat can be good to familiarize yourself with.
By practicing such scenarios, you can boost your confidence and make your travel experience smoother and more enjoyable – potentially removing any stress or confusion that can come with travel.
5. Storytelling practice
Engaging in the practice of storytelling, be it in the form of personal stories or fictional tales, can greatly enhance one's linguistic skills and aptitude for storytelling. , an organization dedicated to preserving and sharing the authentic narratives of everyday people, provides an exceptional opportunity for individuals to learn and grow from the raw and unfiltered experiences of others.
By immersing yourself in genuine stories, you can gain invaluable insights into people’s use of the English language and the nuances of effective storytelling. Being a good storyteller can also help you with other essential skills, like pitching and selling ideas.
6. Conflict resolution
Enhancing your language skills in negotiation, empathy, and communication can be attained through the consistent practice of conflict resolution scenarios. If you are looking to acquire a comprehensive understanding of conflict resolution methods and techniques, then the "" guide is an excellent resource to consult. This guide offers a detailed and thorough overview of various conflict resolution techniques that can be employed in a variety of settings, helping you to also practice your English.
Having strong conflict resolution skills in English can help you in many scenarios, from workplace conflict to a disagreement between friends or strangers. You can try looking at common conflicts you see on the tv/film/internet or come across in real life and practice how you would personally approach it and what kinds of things you would say.Ěý
7. Academic presentations
To enhance your ability to communicate in English effectively and coherently in public, consider taking part in academic-style presentations. , a platform that offers a diverse range of educational videos covering various topics, can serve as an excellent resource for honing your presentation skills. By utilizing TED-Ed's resources, you can gain valuable experience and confidence in delivering presentations with clarity and precision.
You could try filming yourself giving the presentation, critique areas for improvement, or ask your friends for feedback. If you’re feeling particularly brave, even posting it online for feedback. For extra help with your confidence, there are to help you with your public speaking.
8. Negotiation
If you're looking to improve your English language skills in a business context, one of the most important aspects to practice is negotiating. Negotiating prices, terms, and agreements effectively can lead to better outcomes for everyone. From negotiating the price of fruit at a market to negotiating your job's salary, negotiation is a huge part of people’s lives and knowing how to confidently negotiate in English is important.
The provides resources, including thorough articles and guides that are designed to help you hone your negotiation skills. By utilizing resources like these, you can gain the knowledge and confidence needed to succeed in any business negotiation. Watch business-related and TV shows, watching how they negotiate and what sort of language they use. Take note of commonly asked questions relevant to your situation, so you are prepared for what someone might ask you.Ěý
By placing yourself in realistic practice scenarios, you can transform your language learning experience. Remember, consistent practice and a willingness to step out of your comfort zone are key to becoming a more proficient English speaker. Embrace these opportunities to interact with the language in diverse contexts, situations and watch your language confidence grow.